A group of Cockcroft Institute scientists led by Lee Jones has published an article in the Review of Scientific Instruments summarising years of work in the development of the Transverse Energy Spread Spectrometer (TESS) apparatus at Daresbury Laboratory.
The TESS measures the transverse energy distribution curve (TEDC) of photoelectrons emitted from a photocathode, and from this TEDC, the mean transverse energy (MTE) of the emitted electrons can be derived. These measurements are essential to characterize the intrinsic emittance of the photocathodes used as electron sources in particle accelerators, which determine the minimum achievable particle beam emittance in an electron accelerator.
The minimization of the mean transverse energy is crucial to reduce the electron beam emittance and thus generate a high-brightness beam. For instance, reducing the emittance in an accelerator that drives a Free-Electron Laser (FEL) delivers a significant reduction in the saturation length for an x-ray FEL, thus reducing the machine’s construction footprint and operating costs while increasing the brightness of the x-ray beam.
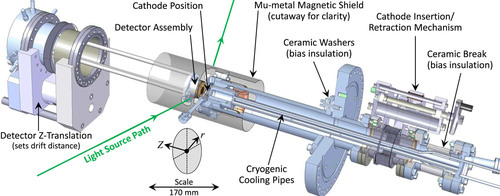
The original TESS instrument used laser modules to illuminate a photocathode at a single specific wavelength, so work with pure metals (for example) was not possible due to the nonavailability of such UV laser modules.
The upgraded TESS system incorporates a number of advancements and modifications to the experimental setup, including a laser-driven plasma broadband light source coupled to a twin-grating monochromator with various output aperture sizes, a revised photoemission detector with increased electron transmission, and the ability to cryogenically cool the photocathode under test.
Collectively, the advances reported in the article increase both the range of photocathode types that can be characterized and the detection sensitivity compared to the original TESS. Furthermore, the ability to measure energy spread at any illumination wavelength for pure metal, alkali/bialkali metal or semiconductor photocathodes is a significant advance over the previous TESS.
The article presents a complete description of the TESS experimental system, data acquisition and analysis, and an assessment of the experimental errors. The article includes values for the MTE extracted from transverse energy distribution curve measurements for copper (100), (110), and (111) single-crystal photocathodes illuminated at UV wavelengths around 266 nm.
Reference
L. B. Jones, D. P. Juarez-Lopez, H. E. Scheibler, A. S. Terekhov, B. L. Militsyn, C. P. Welsch, and T. C. Q. Noakes, “The measurement of photocathode transverse energy distribution curves (TEDCs) using the transverse energy spread spectrometer (TESS) experimental system”, Review of Scientific Instruments 93, 113314 (2022)
